docs: regenerated to align with changed, added and removed options
This commit is contained in:
parent
41f4c6ae01
commit
26a904f861
12
README.md
12
README.md
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
|||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||
<img src=".github/logo.png" alt="Quickemu" width="256" />
|
||||
|
||||
# Quickemu
|
||||
|
|
@ -7,17 +6,16 @@
|
|||
**Quickly create and run optimised Windows, macOS and Linux virtual machines:**
|
||||
|
||||
**Made with 💝 for <img src=".github/tux.png" align="top" width="24" alt="Tux (Linux)"/>**
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://wimpysworld.io/discord" target="_blank"><img alt="Discord" src="https://img.shields.io/discord/712850672223125565?style=for-the-badge&logo=discord&logoColor=%23ffffff&label=Discord&labelColor=%234253e8
|
||||
&color=%23e4e2e2"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://fosstodon.org/@wimpy" target="_blank"><img alt="Mastodon" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Mastodon-6468fa?style=for-the-badge&logo=mastodon&logoColor=%23ffffff"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://twitter.com/m_wimpress" target="_blank"><img alt="Twitter" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Twitter-303030?style=for-the-badge&logo=x&logoColor=%23ffffff"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://linkedin.com/in/martinwimpress" target="_blank"><img alt="LinkedIn" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/LinkedIn-1667be?style=for-the-badge&logo=linkedin&logoColor=%23ffffff"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://wimpysworld.io/discord" target="_blank"><img alt="Discord" src="https://img.shields.io/discord/712850672223125565?style=for-the-badge&logo=discord&logoColor=%23ffffff&label=Discord&labelColor=%234253e8&color=%23e4e2e2"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://fosstodon.org/@wimpy" target="_blank"><img alt="Mastodon" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Mastodon-6468fa?style=for-the-badge&logo=mastodon&logoColor=%23ffffff"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://twitter.com/m_wimpress" target="_blank"><img alt="Twitter" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Twitter-303030?style=for-the-badge&logo=x&logoColor=%23ffffff"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://linkedin.com/in/martinwimpress" target="_blank"><img alt="LinkedIn" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/LinkedIn-1667be?style=for-the-badge&logo=linkedin&logoColor=%23ffffff"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
**Quickemu** is a wrapper for the excellent [QEMU](https://www.qemu.org/) that
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1 +1 @@
|
|||
Subproject commit bcde95902676cb7c1918eb71753724ffcf641e6e
|
||||
Subproject commit 91309a4efd67c29fe44f103fa78d82cd71beaf78
|
||||
189
docs/quickemu.1
189
docs/quickemu.1
|
|
@ -10,133 +10,137 @@ quickemu \- A quick VM builder and manager
|
|||
machines for Linux, macOS and Windows
|
||||
.SH OPTIONS
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]vm\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-vm\f[R]
|
||||
vm configuration file
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
You can also pass optional parameters
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]access\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-access\f[R]
|
||||
Enable remote spice access support.
|
||||
`local' (default), `remote', `clientipaddress'
|
||||
\[oq]local\[cq] (default), \[oq]remote\[cq], \[oq]clientipaddress\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]braille\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-braille\f[R]
|
||||
Enable braille support.
|
||||
Requires SDL.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]delete\-disk\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-delete\-disk\f[R]
|
||||
Delete the disk image and EFI variables
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]delete\-vm\f[R]
|
||||
Delete the entire VM and it\[cq]s configuration
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-delete\-vm\f[R]
|
||||
Delete the entire VM and its configuration
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]display\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-display\f[R]
|
||||
Select display backend.
|
||||
`sdl' (default), `gtk', `none', `spice' or `spice\-app'
|
||||
\[oq]sdl\[cq] (default), \[oq]gtk\[cq], \[oq]none\[cq], \[oq]spice\[cq]
|
||||
or \[oq]spice\-app\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]fullscreen\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-fullscreen\f[R]
|
||||
Starts VM in full screen mode (Ctl+Alt+f to exit)
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]ignore\-msrs\-always\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-ignore\-msrs\-always\f[R]
|
||||
Configure KVM to always ignore unhandled machine\-specific registers
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]screen <screen>\f[R]
|
||||
Use specified screen to determine the window size.
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-kill\f[R]
|
||||
Kill the VM process if it is running
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]screenpct <percent>\f[R]
|
||||
Percent of fullscreen for VM if \[en]fullscreen is not specified.
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-offline\f[R]
|
||||
Override all network settings and start the VM offline
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]shortcut\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-shortcut\f[R]
|
||||
Create a desktop shortcut
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]snapshot apply <tag>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-snapshot apply <tag>\f[R]
|
||||
Apply/restore a snapshot.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]snapshot create <tag>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-snapshot create <tag>\f[R]
|
||||
Create a snapshot.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]snapshot delete <tag>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-snapshot delete <tag>\f[R]
|
||||
Delete a snapshot.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]snapshot info\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-snapshot info\f[R]
|
||||
Show disk/snapshot info.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]status\-quo\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-status\-quo\f[R]
|
||||
Do not commit any changes to disk/snapshot.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]viewer <viewer>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-viewer <viewer>\f[R]
|
||||
Choose an alternative viewer.
|
||||
\[at]Options: `spicy' (default), `remote\-viewer', `none'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[oq]spicy\[cq] (default), \[oq]remote\-viewer\[cq],
|
||||
\[oq]none\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]width <width>\f[R]
|
||||
Set VM screen width.
|
||||
Does nothing without \[en]height
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-width <width>\f[R]
|
||||
Set VM screen width; requires \[oq]\-\-height\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]height <height>\f[R]
|
||||
Set VM screen height.
|
||||
Does nothing without \[en]width
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-height <height>\f[R]
|
||||
Set VM screen height; requires \[oq]\-\-width\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]ssh\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
Set ssh\-port manually
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-ssh\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
Set SSH port manually
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]spice\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
Set spice\-port manually
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-spice\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
Set SPICE port manually
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]public\-dir <path>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-public\-dir <path>\f[R]
|
||||
Expose share directory.
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[cq]\[cq] (default: xdg\-user\-dir PUBLICSHARE), `',
|
||||
`none'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[cq]\[cq] (default: xdg\-user\-dir PUBLICSHARE),
|
||||
\[oq]\[cq], \[oq]none\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]monitor <type>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-monitor <type>\f[R]
|
||||
Set monitor connection type.
|
||||
\[at]Options: `socket' (default), `telnet', `none'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[oq]socket\[cq] (default), \[oq]telnet\[cq],
|
||||
\[oq]none\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]monitor\-telnet\-host <ip/host>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-monitor\-telnet\-host <ip/host>\f[R]
|
||||
Set telnet host for monitor.
|
||||
(default: `localhost')
|
||||
(default: \[oq]localhost\[cq])
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]monitor\-telnet\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-monitor\-telnet\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
Set telnet port for monitor.
|
||||
(default: `4440')
|
||||
(default: \[oq]4440\[cq])
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]monitor\-cmd <cmd>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-monitor\-cmd <cmd>\f[R]
|
||||
Send command to monitor if available.
|
||||
(Example: system_powerdown)
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]serial <type>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-serial <type>\f[R]
|
||||
Set serial connection type.
|
||||
\[at]Options: `socket' (default), `telnet', `none'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[oq]socket\[cq] (default), \[oq]telnet\[cq],
|
||||
\[oq]none\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]serial\-telnet\-host <ip/host>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-serial\-telnet\-host <ip/host>\f[R]
|
||||
Set telnet host for serial.
|
||||
(default: `localhost')
|
||||
(default: \[oq]localhost\[cq])
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]serial\-telnet\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-serial\-telnet\-port <port>\f[R]
|
||||
Set telnet port for serial.
|
||||
(default: `6660')
|
||||
(default: \[oq]6660\[cq])
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]keyboard <type>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-keyboard <type>\f[R]
|
||||
Set keyboard.
|
||||
\[at]Options: `usb' (default), `ps2', `virtio'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[oq]usb\[cq] (default), \[oq]ps2\[cq], \[oq]virtio\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]keyboard_layout <layout>\f[R]
|
||||
Set keyboard layout.
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-keyboard_layout <layout>\f[R]
|
||||
Set keyboard layout: \[oq]en\-us\[cq] (default)
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]mouse <type>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-mouse <type>\f[R]
|
||||
Set mouse.
|
||||
\[at]Options: `tablet' (default), `ps2', `usb', `virtio'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[oq]tablet\[cq] (default), \[oq]ps2\[cq], \[oq]usb\[cq],
|
||||
\[oq]virtio\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]usb\-controller <type>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-usb\-controller <type>\f[R]
|
||||
Set usb\-controller.
|
||||
\[at]Options: `ehci' (default), `xhci', `none'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[oq]ehci\[cq] (default), \[oq]xhci\[cq], \[oq]none\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]sound\-card <type>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-sound\-card <type>\f[R]
|
||||
Set sound card.
|
||||
\[at]Options: `intel\-hda' (default), `ac97', `es1370', `sb16', `none'
|
||||
\[at]Options: \[oq]intel\-hda\[cq] (default), \[oq]ac97\[cq],
|
||||
\[oq]es1370\[cq], \[oq]sb16\[cq], \[oq]none\[cq]
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]extra_args <arguments>\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-extra_args <arguments>\f[R]
|
||||
Pass additional arguments to qemu
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\[en]version\f[R]
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-version\f[R]
|
||||
Print version
|
||||
.SH EXAMPLES
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
|
|
@ -431,7 +435,7 @@ While \f[CR]quickemu\f[R] and \f[CR]quickget\f[R] are designed for the
|
|||
terminal, a graphical user interface is also available:
|
||||
.IP \[bu] 2
|
||||
\f[B]\c
|
||||
.UR https://github.com/quickgui/quickgui
|
||||
.UR https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickgui
|
||||
Quickgui
|
||||
.UE \c
|
||||
\f[R] by \c
|
||||
|
|
@ -480,12 +484,6 @@ qqX
|
|||
Alex Genovese
|
||||
.UE \c
|
||||
\ (see the github pages)
|
||||
[IMAGE: \c
|
||||
.UR https://github.com/TuxVinyards/qqX/assets/3956806/18e5c495-8072-49a5-8b9c-e1302549efcf
|
||||
qqX\-vmm
|
||||
.UE \c
|
||||
]
|
||||
qqX\-vmm
|
||||
.SS Creating Linux guests 🐧
|
||||
.SS Ubuntu
|
||||
\f[CR]quickget\f[R] will automatically download an Ubuntu release and
|
||||
|
|
@ -1137,7 +1135,7 @@ Arguments
|
|||
\-\-access : Enable remote spice access support. \[aq]local\[aq] (default), \[aq]remote\[aq], \[aq]clientipaddress\[aq]
|
||||
\-\-braille : Enable braille support. Requires SDL.
|
||||
\-\-delete\-disk : Delete the disk image and EFI variables
|
||||
\-\-delete\-vm : Delete the entire VM and it\[aq]s configuration
|
||||
\-\-delete\-vm : Delete the entire VM and its configuration
|
||||
\-\-display : Select display backend. \[aq]sdl\[aq] (default), \[aq]gtk\[aq], \[aq]none\[aq], \[aq]spice\[aq] or \[aq]spice\-app\[aq]
|
||||
\-\-fullscreen : Starts VM in full screen mode (Ctl+Alt+f to exit)
|
||||
\-\-ignore\-msrs\-always : Configure KVM to always ignore unhandled machine\-specific registers
|
||||
|
|
@ -1178,59 +1176,6 @@ Here is an example of how to create a shortcut.
|
|||
.EX
|
||||
quickemu \-\-vm ubuntu\-22.04\-desktop.conf \-\-shortcut
|
||||
.EE
|
||||
.SS Screen and window size (Linux guests only)
|
||||
\f[CR]qemu\f[R] will always default to the primary monitor to display
|
||||
the VM\[cq]s window.
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
Without the \f[CR]\-\-screen\f[R] option, \f[CR]quickemu\f[R] will look
|
||||
for the size of the smallest monitor, and use a size that fits on said
|
||||
monitor.
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
The \f[CR]\-\-screen\f[R] option forces \f[CR]quickemu\f[R] to use the
|
||||
size of the given monitor to compute the size of the window.
|
||||
\f[B]It won\[cq]t use that monitor to display the VM\[cq]s window if
|
||||
it\[cq]s not the primary monitor\f[R].
|
||||
This is useful if the primary monitor if not the smallest one, and if
|
||||
the VM\[cq]s window doesn\[cq]t need to be moved around.
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
The \f[CR]\-\-screen\f[R] option is also useful with the
|
||||
\f[CR]\-\-fullscreen\f[R] option, again because \f[CR]qemu\f[R] will
|
||||
always use the primary monitor.
|
||||
In order for the fullscreen mode to work properly, the resolution of the
|
||||
VM\[cq]s window must match the resolution of the screen.
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
To know which screen to use, type:
|
||||
.IP
|
||||
.EX
|
||||
xrandr \-\-listmonitors | grep \-v Monitors
|
||||
.EE
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
The command will output something like this:
|
||||
.IP
|
||||
.EX
|
||||
0: +*HDMI\-0 2560/597x1440/336+1920+0 HDMI\-0
|
||||
1: +DVI\-D\-0 1920/527x1080/296+0+0 DVI\-D\-0
|
||||
.EE
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
The first number is what needs to be passed to the \f[CR]\-\-screen\f[R]
|
||||
option.
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
.IP
|
||||
.EX
|
||||
quickemu \-\-vm vm.conf \-\-screen 0
|
||||
.EE
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
The above uses the 2560x1440 screen to compute the size of the window,
|
||||
which Quickemu sizes to 2048x1152.
|
||||
Without the \f[CR]\-\-screen\f[R] option, Quickemu would have used the
|
||||
1920x1080 monitor which results in a window size of 1664x936.
|
||||
.PP
|
||||
The `\[en]screenpct' is an optional integer value between 25 <= pct <
|
||||
100 which will override system default screen sizes.
|
||||
The VM size will be `pct' of the chosen screen.
|
||||
\f[B]If \[en]fullscreen is chosen screen will be fullsize instead of
|
||||
being scaled down by \[en]screenpct value.\f[R]
|
||||
.SS References
|
||||
Useful reference that assisted the development of Quickemu.
|
||||
.IP \[bu] 2
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ quickemu - A quick VM builder and manager
|
|||
|
||||
# SYNOPSIS
|
||||
|
||||
**quickemu** \[*OPTION*\]...
|
||||
**quickemu** \[*OPTION*\]…
|
||||
|
||||
# DESCRIPTION
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,8 +28,8 @@ machines for Linux, macOS and Windows
|
|||
You can also pass optional parameters
|
||||
|
||||
**--access**
|
||||
: Enable remote spice access support. 'local' (default), 'remote',
|
||||
'clientipaddress'
|
||||
: Enable remote spice access support. ‘local’ (default), ‘remote’,
|
||||
‘clientipaddress’
|
||||
|
||||
**--braille**
|
||||
: Enable braille support. Requires SDL.
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,11 +38,11 @@ You can also pass optional parameters
|
|||
: Delete the disk image and EFI variables
|
||||
|
||||
**--delete-vm**
|
||||
: Delete the entire VM and it's configuration
|
||||
: Delete the entire VM and its configuration
|
||||
|
||||
**--display**
|
||||
: Select display backend. 'sdl' (default), 'gtk', 'none', 'spice' or
|
||||
'spice-app'
|
||||
: Select display backend. ‘sdl’ (default), ‘gtk’, ‘none’, ‘spice’ or
|
||||
‘spice-app’
|
||||
|
||||
**--fullscreen**
|
||||
: Starts VM in full screen mode (Ctl+Alt+f to exit)
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,11 +50,11 @@ You can also pass optional parameters
|
|||
**--ignore-msrs-always**
|
||||
: Configure KVM to always ignore unhandled machine-specific registers
|
||||
|
||||
**--screen \<screen\>**
|
||||
: Use specified screen to determine the window size.
|
||||
**--kill**
|
||||
: Kill the VM process if it is running
|
||||
|
||||
**--screenpct \<percent\>**
|
||||
: Percent of fullscreen for VM if --fullscreen is not specified.
|
||||
**--offline**
|
||||
: Override all network settings and start the VM offline
|
||||
|
||||
**--shortcut**
|
||||
: Create a desktop shortcut
|
||||
|
|
@ -75,63 +75,63 @@ You can also pass optional parameters
|
|||
: Do not commit any changes to disk/snapshot.
|
||||
|
||||
**--viewer \<viewer\>**
|
||||
: Choose an alternative viewer. @Options: 'spicy' (default),
|
||||
'remote-viewer', 'none'
|
||||
: Choose an alternative viewer. @Options: ‘spicy’ (default),
|
||||
‘remote-viewer’, ‘none’
|
||||
|
||||
**--width \<width\>**
|
||||
: Set VM screen width. Does nothing without --height
|
||||
: Set VM screen width; requires ‘--height’
|
||||
|
||||
**--height \<height\>**
|
||||
: Set VM screen height. Does nothing without --width
|
||||
: Set VM screen height; requires ‘--width’
|
||||
|
||||
**--ssh-port \<port\>**
|
||||
: Set ssh-port manually
|
||||
: Set SSH port manually
|
||||
|
||||
**--spice-port \<port\>**
|
||||
: Set spice-port manually
|
||||
: Set SPICE port manually
|
||||
|
||||
**--public-dir \<path\>**
|
||||
: Expose share directory. @Options: '' (default: xdg-user-dir
|
||||
PUBLICSHARE), '`<directory>`{=html}', 'none'
|
||||
: Expose share directory. @Options: ’’ (default: xdg-user-dir
|
||||
PUBLICSHARE), ‘<directory>’, ‘none’
|
||||
|
||||
**--monitor \<type\>**
|
||||
: Set monitor connection type. @Options: 'socket' (default), 'telnet',
|
||||
'none'
|
||||
: Set monitor connection type. @Options: ‘socket’ (default), ‘telnet’,
|
||||
‘none’
|
||||
|
||||
**--monitor-telnet-host \<ip/host\>**
|
||||
: Set telnet host for monitor. (default: 'localhost')
|
||||
: Set telnet host for monitor. (default: ‘localhost’)
|
||||
|
||||
**--monitor-telnet-port \<port\>**
|
||||
: Set telnet port for monitor. (default: '4440')
|
||||
: Set telnet port for monitor. (default: ‘4440’)
|
||||
|
||||
**--monitor-cmd \<cmd\>**
|
||||
: Send command to monitor if available. (Example: system_powerdown)
|
||||
|
||||
**--serial \<type\>**
|
||||
: Set serial connection type. @Options: 'socket' (default), 'telnet',
|
||||
'none'
|
||||
: Set serial connection type. @Options: ‘socket’ (default), ‘telnet’,
|
||||
‘none’
|
||||
|
||||
**--serial-telnet-host \<ip/host\>**
|
||||
: Set telnet host for serial. (default: 'localhost')
|
||||
: Set telnet host for serial. (default: ‘localhost’)
|
||||
|
||||
**--serial-telnet-port \<port\>**
|
||||
: Set telnet port for serial. (default: '6660')
|
||||
: Set telnet port for serial. (default: ‘6660’)
|
||||
|
||||
**--keyboard \<type\>**
|
||||
: Set keyboard. @Options: 'usb' (default), 'ps2', 'virtio'
|
||||
: Set keyboard. @Options: ‘usb’ (default), ‘ps2’, ‘virtio’
|
||||
|
||||
**--keyboard_layout \<layout\>**
|
||||
: Set keyboard layout.
|
||||
: Set keyboard layout: ‘en-us’ (default)
|
||||
|
||||
**--mouse \<type\>**
|
||||
: Set mouse. @Options: 'tablet' (default), 'ps2', 'usb', 'virtio'
|
||||
: Set mouse. @Options: ‘tablet’ (default), ‘ps2’, ‘usb’, ‘virtio’
|
||||
|
||||
**--usb-controller \<type\>**
|
||||
: Set usb-controller. @Options: 'ehci' (default), 'xhci', 'none'
|
||||
: Set usb-controller. @Options: ‘ehci’ (default), ‘xhci’, ‘none’
|
||||
|
||||
**--sound-card \<type\>**
|
||||
: Set sound card. @Options: 'intel-hda' (default), 'ac97', 'es1370',
|
||||
'sb16', 'none'
|
||||
: Set sound card. @Options: ‘intel-hda’ (default), ‘ac97’, ‘es1370’,
|
||||
‘sb16’, ‘none’
|
||||
|
||||
**--extra_args \<arguments\>**
|
||||
: Pass additional arguments to qemu
|
||||
|
|
@ -141,21 +141,21 @@ You can also pass optional parameters
|
|||
|
||||
# EXAMPLES
|
||||
|
||||
**quickemu --vm ubuntu-mate-22.04.conf**
|
||||
**quickemu –vm ubuntu-mate-22.04.conf**
|
||||
: Launches the VM specified in the file *ubuntu-mate-22.04.conf*
|
||||
|
||||
# Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
**Quickemu** is a wrapper for the excellent
|
||||
[QEMU](https://www.qemu.org/) that automatically *"does the right
|
||||
thing"* when creating virtual machines. No requirement for exhaustive
|
||||
[QEMU](https://www.qemu.org/) that automatically *“does the right
|
||||
thing”* when creating virtual machines. No requirement for exhaustive
|
||||
configuration options. You decide what operating system you want to run
|
||||
and Quickemu takes care of the rest 🤖
|
||||
|
||||
- `quickget` **automatically downloads the upstream OS** and creates
|
||||
the configuration 📀
|
||||
- `quickemu` enumerates your hardware and launches the virtual machine
|
||||
with the **optimum configuration best suited to your computer** ⚡️
|
||||
- `quickget` **automatically downloads the upstream OS** and creates the
|
||||
configuration 📀
|
||||
- `quickemu` enumerates your hardware and launches the virtual machine
|
||||
with the **optimum configuration best suited to your computer** ⚡️
|
||||
|
||||
The original objective of the project was to [enable quick testing of
|
||||
Linux
|
||||
|
|
@ -172,57 +172,56 @@ Haiku, KolibriOS, OpenIndiana, ReactOS, and more.
|
|||
|
||||
# Features
|
||||
|
||||
- **macOS** Sonoma, Ventura, Monterey, Big Sur, Catalina & Mojave
|
||||
- **Windows** 10 and 11 including TPM 2.0
|
||||
- **Windows Server** 2022 2019 2016 2012-r2
|
||||
- [Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/desktop) and all the **[official Ubuntu
|
||||
flavours](https://ubuntu.com/download/flavours)**
|
||||
- **Nearly 1000 operating system editions are supported!**
|
||||
- Full SPICE support including host/guest clipboard sharing
|
||||
- VirtIO-webdavd file sharing for Linux and Windows guests
|
||||
- VirtIO-9p file sharing for Linux and macOS guests
|
||||
- [QEMU Guest Agent
|
||||
support](https://wiki.qemu.org/Features/GuestAgent); provides access
|
||||
to a system-level agent via standard QMP commands
|
||||
- Samba file sharing for Linux, macOS and Windows guests (*if `smbd`
|
||||
is installed on the host*)
|
||||
- VirGL acceleration
|
||||
- USB device pass-through
|
||||
- Smartcard pass-through
|
||||
- Automatic SSH port forwarding to guests
|
||||
- Network port forwarding
|
||||
- Full duplex audio
|
||||
- Braille support
|
||||
- EFI (with or without SecureBoot) and Legacy BIOS boot
|
||||
- **macOS** Sonoma, Ventura, Monterey, Big Sur, Catalina & Mojave
|
||||
- **Windows** 10 and 11 including TPM 2.0
|
||||
- **Windows Server** 2022 2019 2016 2012-r2
|
||||
- [Ubuntu](https://ubuntu.com/desktop) and all the **[official Ubuntu
|
||||
flavours](https://ubuntu.com/download/flavours)**
|
||||
- **Nearly 1000 operating system editions are supported!**
|
||||
- Full SPICE support including host/guest clipboard sharing
|
||||
- VirtIO-webdavd file sharing for Linux and Windows guests
|
||||
- VirtIO-9p file sharing for Linux and macOS guests
|
||||
- [QEMU Guest Agent support](https://wiki.qemu.org/Features/GuestAgent);
|
||||
provides access to a system-level agent via standard QMP commands
|
||||
- Samba file sharing for Linux, macOS and Windows guests (*if `smbd` is
|
||||
installed on the host*)
|
||||
- VirGL acceleration
|
||||
- USB device pass-through
|
||||
- Smartcard pass-through
|
||||
- Automatic SSH port forwarding to guests
|
||||
- Network port forwarding
|
||||
- Full duplex audio
|
||||
- Braille support
|
||||
- EFI (with or without SecureBoot) and Legacy BIOS boot
|
||||
|
||||
When installing from source, you will need to install the following
|
||||
requirements manually:
|
||||
|
||||
- [QEMU](https://www.qemu.org/) (*6.0.0 or newer*) **with GTK, SDL,
|
||||
SPICE & VirtFS support**
|
||||
- [bash](https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/) (*4.0 or newer*)
|
||||
- [Coreutils](https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/)
|
||||
- [curl](https://curl.se/)
|
||||
- [EDK II](https://github.com/tianocore/edk2)
|
||||
- [gawk](https://www.gnu.org/software/gawk/)
|
||||
- [grep](https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/)
|
||||
- [glxinfo](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/mesa/demos)
|
||||
- [jq](https://stedolan.github.io/jq/)
|
||||
- [LSB](https://wiki.linuxfoundation.org/lsb/start)
|
||||
- [pciutils](https://github.com/pciutils/pciutils)
|
||||
- [procps](https://gitlab.com/procps-ng/procps)
|
||||
- [python3](https://www.python.org/)
|
||||
- [mkisofs](http://cdrtools.sourceforge.net/private/cdrecord.html)
|
||||
- [usbutils](https://github.com/gregkh/usbutils)
|
||||
- [util-linux](https://github.com/karelzak/util-linux)
|
||||
- [sed](https://www.gnu.org/software/sed/)
|
||||
- [socat](http://www.dest-unreach.org/socat/)
|
||||
- [spicy](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/spice/spice-gtk)
|
||||
- [swtpm](https://github.com/stefanberger/swtpm)
|
||||
- [xdg-user-dirs](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/xdg-user-dirs/)
|
||||
- [xrandr](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/xorg/app/xrandr)
|
||||
- [zsync](http://zsync.moria.org.uk/)
|
||||
- [unzip](http://www.info-zip.org/UnZip.html)
|
||||
- [QEMU](https://www.qemu.org/) (*6.0.0 or newer*) **with GTK, SDL,
|
||||
SPICE & VirtFS support**
|
||||
- [bash](https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/) (*4.0 or newer*)
|
||||
- [Coreutils](https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/)
|
||||
- [curl](https://curl.se/)
|
||||
- [EDK II](https://github.com/tianocore/edk2)
|
||||
- [gawk](https://www.gnu.org/software/gawk/)
|
||||
- [grep](https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/)
|
||||
- [glxinfo](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/mesa/demos)
|
||||
- [jq](https://stedolan.github.io/jq/)
|
||||
- [LSB](https://wiki.linuxfoundation.org/lsb/start)
|
||||
- [pciutils](https://github.com/pciutils/pciutils)
|
||||
- [procps](https://gitlab.com/procps-ng/procps)
|
||||
- [python3](https://www.python.org/)
|
||||
- [mkisofs](http://cdrtools.sourceforge.net/private/cdrecord.html)
|
||||
- [usbutils](https://github.com/gregkh/usbutils)
|
||||
- [util-linux](https://github.com/karelzak/util-linux)
|
||||
- [sed](https://www.gnu.org/software/sed/)
|
||||
- [socat](http://www.dest-unreach.org/socat/)
|
||||
- [spicy](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/spice/spice-gtk)
|
||||
- [swtpm](https://github.com/stefanberger/swtpm)
|
||||
- [xdg-user-dirs](https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/xdg-user-dirs/)
|
||||
- [xrandr](https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/xorg/app/xrandr)
|
||||
- [zsync](http://zsync.moria.org.uk/)
|
||||
- [unzip](http://www.info-zip.org/UnZip.html)
|
||||
|
||||
For Ubuntu, Arch and NixOS hosts, the
|
||||
[ppa](https://launchpad.net/~flexiondotorg/+archive/ubuntu/quickemu),
|
||||
|
|
@ -296,9 +295,9 @@ brew install qemu bash coreutils curl grep jq pciutils python@3.10 cdrtools gnu-
|
|||
While `quickemu` and `quickget` are designed for the terminal, a
|
||||
graphical user interface is also available:
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Quickgui](https://github.com/quickgui/quickgui)** by [Mark
|
||||
Johnson](https://github.com/marxjohnson) and [Yannick
|
||||
Mauray](https://github.com/ymauray).
|
||||
- **[Quickgui](https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickgui)** by [Mark
|
||||
Johnson](https://github.com/marxjohnson) and [Yannick
|
||||
Mauray](https://github.com/ymauray).
|
||||
|
||||
To install Quickgui on Ubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -319,11 +318,16 @@ There is also a multi option desktop integrated text interface, the
|
|||
unique tools and utilities to help you make light work of installations,
|
||||
snapshots and disk management
|
||||
|
||||
- **[qqX](https://github.com/TuxVinyards/qqX)** is independently
|
||||
curated by [Alex Genovese](https://github.com/TuxVinyards) (see the
|
||||
github pages)
|
||||
- **[qqX](https://github.com/TuxVinyards/qqX)** is independently curated
|
||||
by [Alex Genovese](https://github.com/TuxVinyards) (see the github
|
||||
pages)
|
||||
|
||||
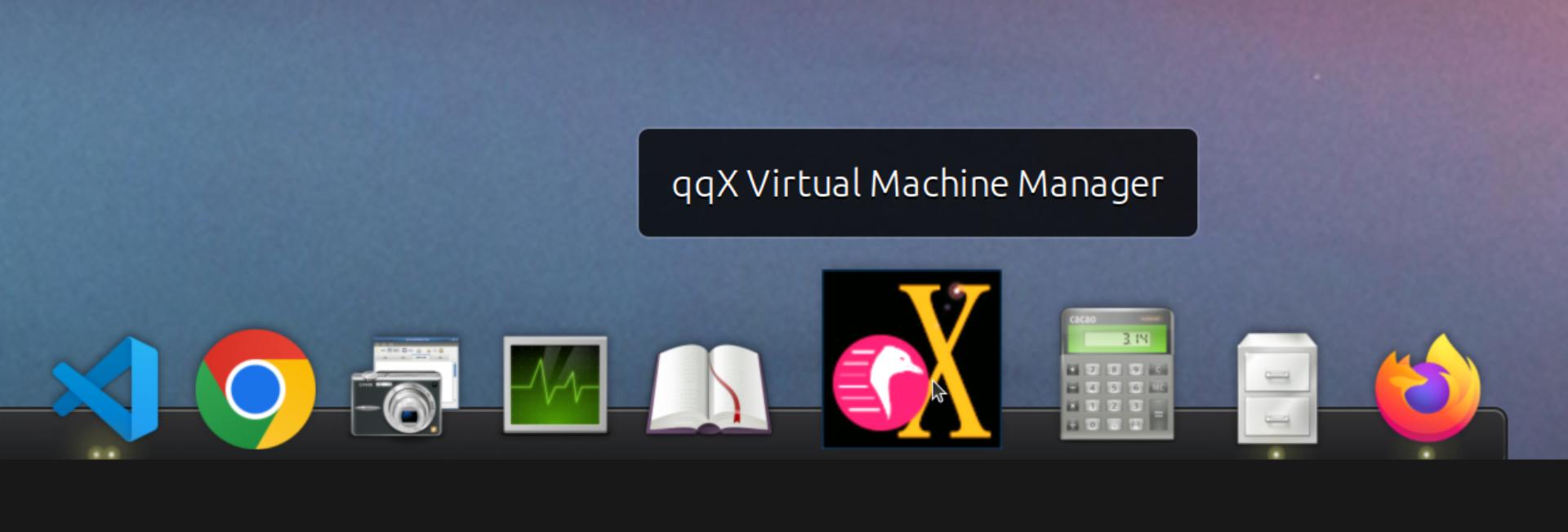
|
||||
<figure>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
src="https://github.com/TuxVinyards/qqX/assets/3956806/18e5c495-8072-49a5-8b9c-e1302549efcf"
|
||||
alt="qqX-vmm" />
|
||||
<figcaption aria-hidden="true">qqX-vmm</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating Linux guests 🐧
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -337,14 +341,14 @@ quickget ubuntu 22.04
|
|||
quickemu --vm ubuntu-22.04.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-vdagent`
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-webdavd`
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-vdagent`
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-webdavd`
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu daily-live images
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -369,18 +373,18 @@ The project
|
|||
[wiki](https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickemu/wiki/02-Create-Linux-virtual-machines)
|
||||
may have further information.
|
||||
|
||||
- `edubuntu` (Edubuntu)
|
||||
- `kubuntu` (Kubuntu)
|
||||
- `lubuntu` (Lubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-budgie` (Ubuntu Budgie)
|
||||
- `ubuntucinnamon` (Ubuntu Cinnamon)
|
||||
- `ubuntukylin` (Ubuntu Kylin)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-mate` (Ubuntu MATE)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-server` (Ubuntu Server)
|
||||
- `ubuntustudio` (Ubuntu Studio)
|
||||
- `ubuntu` (Ubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-unity` (Ubuntu Unity)
|
||||
- `xubuntu` (Xubuntu)
|
||||
- `edubuntu` (Edubuntu)
|
||||
- `kubuntu` (Kubuntu)
|
||||
- `lubuntu` (Lubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-budgie` (Ubuntu Budgie)
|
||||
- `ubuntucinnamon` (Ubuntu Cinnamon)
|
||||
- `ubuntukylin` (Ubuntu Kylin)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-mate` (Ubuntu MATE)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-server` (Ubuntu Server)
|
||||
- `ubuntustudio` (Ubuntu Studio)
|
||||
- `ubuntu` (Ubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-unity` (Ubuntu Unity)
|
||||
- `xubuntu` (Xubuntu)
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use `quickget` with advanced options :
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -421,96 +425,96 @@ Further information is available from the project
|
|||
|
||||
`quickget` also supports:
|
||||
|
||||
- `alma` (AlmaLinux)
|
||||
- `alpine` (Alpine Linux)
|
||||
- `android` (Android x86)
|
||||
- `antix` (Antix)
|
||||
- `archcraft` (Archcraft)
|
||||
- `archlinux` (Arch Linux)
|
||||
- `arcolinux` (Arco Linux)
|
||||
- `artixlinux` (Artix Linux)
|
||||
- `athenaos` (Athena OS)
|
||||
- `batocera` (Batocera)
|
||||
- `bazzite` (Bazzite)
|
||||
- `biglinux` (BigLinux)
|
||||
- `blendos` (BlendOS)
|
||||
- `bodhi` (Bodhi)
|
||||
- `bunsenlabs` (BunsenLabs)
|
||||
- `cachyos` (CachyOS)
|
||||
- `centos-stream` (CentOS Stream)
|
||||
- `chimeralinux` (Chimera Linux)
|
||||
- `crunchbang++` (Crunchbangplusplus)
|
||||
- `debian` (Debian)
|
||||
- `deepin` (Deepin)
|
||||
- `devuan` (Devuan)
|
||||
- `dragonflybsd` (DragonFlyBSD)
|
||||
- `easyos` (EasyOS)
|
||||
- `elementary` (elementary OS)
|
||||
- `endeavouros` (EndeavourOS)
|
||||
- `endless` (Endless OS)
|
||||
- `fedora` (Fedora)
|
||||
- `freebsd` (FreeBSD)
|
||||
- `freedos` (FreeDOS)
|
||||
- `garuda` (Garuda Linux)
|
||||
- `gentoo` (Gentoo)
|
||||
- `ghostbsd` (GhostBSD)
|
||||
- `gnomeos` (GNOME OS)
|
||||
- `guix` (Guix)
|
||||
- `haiku` (Haiku)
|
||||
- `holoiso` (HoloISO)
|
||||
- `kali` (Kali)
|
||||
- `kdeneon` (KDE Neon)
|
||||
- `kolibrios` (KolibriOS)
|
||||
- `linuxlite` (Linux Lite)
|
||||
- `linuxmint` (Linux Mint)
|
||||
- `lmde` (Linux Mint Debian Edition)
|
||||
- `mageia` (Mageia)
|
||||
- `manjaro` (Manjaro)
|
||||
- `mxlinux` (MX Linux)
|
||||
- `netboot` (netboot.xyz)
|
||||
- `netbsd` (NetBSD)
|
||||
- `nitrux` (Nitrux)
|
||||
- `nixos` (NixOS)
|
||||
- `nwg-shell` (nwg-shell)
|
||||
- `openbsd` (OpenBSD)
|
||||
- `openindiana` (OpenIndiana)
|
||||
- `opensuse` (openSUSE)
|
||||
- `oraclelinux` (Oracle Linux)
|
||||
- `parrotsec` (Parrot Security)
|
||||
- `peppermint` (PeppermintOS)
|
||||
- `popos` (Pop!\_OS)
|
||||
- `porteus` (Porteus)
|
||||
- `primtux` (PrimTux)
|
||||
- `pureos` (PureOS)
|
||||
- `reactos` (ReactOS)
|
||||
- `rebornos` (RebornOS)
|
||||
- `rockylinux` (Rocky Linux)
|
||||
- `siduction` (Siduction)
|
||||
- `slackware` (Slackware)
|
||||
- `slax` (Slax)
|
||||
- `slint` (Slint)
|
||||
- `slitaz` (SliTaz)
|
||||
- `solus` (Solus)
|
||||
- `sparkylinux` (SparkyLinux)
|
||||
- `spirallinux` (SpiralLinux)
|
||||
- `tails` (Tails)
|
||||
- `tinycore` (Tiny Core Linux)
|
||||
- `trisquel` (Trisquel-)
|
||||
- `truenas-core` (TrueNAS Core)
|
||||
- `truenas-scale` (TrueNAS Scale)
|
||||
- `tuxedo-os` (Tuxedo OS)
|
||||
- `vanillaos` (Vanilla OS)
|
||||
- `void` (Void Linux)
|
||||
- `vxlinux` (VX Linux)
|
||||
- `zorin` (Zorin OS)
|
||||
- `alma` (AlmaLinux)
|
||||
- `alpine` (Alpine Linux)
|
||||
- `android` (Android x86)
|
||||
- `antix` (Antix)
|
||||
- `archcraft` (Archcraft)
|
||||
- `archlinux` (Arch Linux)
|
||||
- `arcolinux` (Arco Linux)
|
||||
- `artixlinux` (Artix Linux)
|
||||
- `athenaos` (Athena OS)
|
||||
- `batocera` (Batocera)
|
||||
- `bazzite` (Bazzite)
|
||||
- `biglinux` (BigLinux)
|
||||
- `blendos` (BlendOS)
|
||||
- `bodhi` (Bodhi)
|
||||
- `bunsenlabs` (BunsenLabs)
|
||||
- `cachyos` (CachyOS)
|
||||
- `centos-stream` (CentOS Stream)
|
||||
- `chimeralinux` (Chimera Linux)
|
||||
- `crunchbang++` (Crunchbangplusplus)
|
||||
- `debian` (Debian)
|
||||
- `deepin` (Deepin)
|
||||
- `devuan` (Devuan)
|
||||
- `dragonflybsd` (DragonFlyBSD)
|
||||
- `easyos` (EasyOS)
|
||||
- `elementary` (elementary OS)
|
||||
- `endeavouros` (EndeavourOS)
|
||||
- `endless` (Endless OS)
|
||||
- `fedora` (Fedora)
|
||||
- `freebsd` (FreeBSD)
|
||||
- `freedos` (FreeDOS)
|
||||
- `garuda` (Garuda Linux)
|
||||
- `gentoo` (Gentoo)
|
||||
- `ghostbsd` (GhostBSD)
|
||||
- `gnomeos` (GNOME OS)
|
||||
- `guix` (Guix)
|
||||
- `haiku` (Haiku)
|
||||
- `holoiso` (HoloISO)
|
||||
- `kali` (Kali)
|
||||
- `kdeneon` (KDE Neon)
|
||||
- `kolibrios` (KolibriOS)
|
||||
- `linuxlite` (Linux Lite)
|
||||
- `linuxmint` (Linux Mint)
|
||||
- `lmde` (Linux Mint Debian Edition)
|
||||
- `mageia` (Mageia)
|
||||
- `manjaro` (Manjaro)
|
||||
- `mxlinux` (MX Linux)
|
||||
- `netboot` (netboot.xyz)
|
||||
- `netbsd` (NetBSD)
|
||||
- `nitrux` (Nitrux)
|
||||
- `nixos` (NixOS)
|
||||
- `nwg-shell` (nwg-shell)
|
||||
- `openbsd` (OpenBSD)
|
||||
- `openindiana` (OpenIndiana)
|
||||
- `opensuse` (openSUSE)
|
||||
- `oraclelinux` (Oracle Linux)
|
||||
- `parrotsec` (Parrot Security)
|
||||
- `peppermint` (PeppermintOS)
|
||||
- `popos` (Pop!\_OS)
|
||||
- `porteus` (Porteus)
|
||||
- `primtux` (PrimTux)
|
||||
- `pureos` (PureOS)
|
||||
- `reactos` (ReactOS)
|
||||
- `rebornos` (RebornOS)
|
||||
- `rockylinux` (Rocky Linux)
|
||||
- `siduction` (Siduction)
|
||||
- `slackware` (Slackware)
|
||||
- `slax` (Slax)
|
||||
- `slint` (Slint)
|
||||
- `slitaz` (SliTaz)
|
||||
- `solus` (Solus)
|
||||
- `sparkylinux` (SparkyLinux)
|
||||
- `spirallinux` (SpiralLinux)
|
||||
- `tails` (Tails)
|
||||
- `tinycore` (Tiny Core Linux)
|
||||
- `trisquel` (Trisquel-)
|
||||
- `truenas-core` (TrueNAS Core)
|
||||
- `truenas-scale` (TrueNAS Scale)
|
||||
- `tuxedo-os` (Tuxedo OS)
|
||||
- `vanillaos` (Vanilla OS)
|
||||
- `void` (Void Linux)
|
||||
- `vxlinux` (VX Linux)
|
||||
- `zorin` (Zorin OS)
|
||||
|
||||
### [Custom Linux guests](https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickemu/wiki/02-Create-Linux-virtual-machines#manually-create-linux-guests)
|
||||
|
||||
Or you can download a Linux image and manually create a VM
|
||||
configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
- Download a .iso image of a Linux distribution
|
||||
- Create a VM configuration file; for example `debian-bullseye.conf`
|
||||
- Download a .iso image of a Linux distribution
|
||||
- Create a VM configuration file; for example `debian-bullseye.conf`
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
guest_os="linux"
|
||||
|
|
@ -518,18 +522,18 @@ disk_img="debian-bullseye/disk.qcow2"
|
|||
iso="debian-bullseye/firmware-11.0.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `quickemu` to start the virtual machine:
|
||||
- Use `quickemu` to start the virtual machine:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
quickemu --vm debian-bullseye.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection.
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection.
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
|
||||
## Supporting old Linux distros
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -555,62 +559,59 @@ quickemu --vm macos-catalina.conf
|
|||
macOS `mojave`, `catalina`, `big-sur`, `monterey`, `ventura` and
|
||||
`sonoma` are supported.
|
||||
|
||||
- Use cursor keys and enter key to select the **macOS Base System**
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Disk Utility** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Select `QEMU HARDDISK Media` (\~103.08GB) from the list (on
|
||||
Big Sur and above use `Apple Inc. VirtIO Block Device`) and
|
||||
click **Erase**.
|
||||
- Enter a `Name:` for the disk
|
||||
- If you are installing macOS Mojave or later (Catalina, Big
|
||||
Sur, Monterey, Ventura and Sonoma), choose any of the APFS
|
||||
options as the filesystem. MacOS Extended may not work.
|
||||
- Click **Erase**.
|
||||
- Click **Done**.
|
||||
- Close Disk Utility
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Reinstall macOS** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- On the first reboot use cursor keys and enter key to select
|
||||
**macOS Installer**
|
||||
- On the subsequent reboots use cursor keys and enter key to
|
||||
select the disk you named
|
||||
- Once you have finished installing macOS you will be presented with
|
||||
an the out-of-the-box first-start wizard to configure various
|
||||
options and set up your username and password
|
||||
- OPTIONAL: After you have concluded the out-of-the-box wizard, you
|
||||
may want to enable the TRIM feature that the computer industry
|
||||
created for SSD disks. This feature in our macOS installation will
|
||||
allow QuickEmu to compact (shrink) your macOS disk image whenever
|
||||
you delete files inside the Virtual Machine. Without this step your
|
||||
macOS disk image will only ever get larger and will not shrink even
|
||||
when you delete lots of data inside macOS.
|
||||
- To enable TRIM, open the Terminal application and type the
|
||||
following command followed by pressing
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> to tell macos to use the TRIM
|
||||
command on the hard disk when files are deleted:
|
||||
- Use cursor keys and enter key to select the **macOS Base System**
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Disk Utility** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Select `QEMU HARDDISK Media` (~103.08GB) from the list (on Big Sur
|
||||
and above use `Apple Inc. VirtIO Block Device`) and click
|
||||
**Erase**.
|
||||
- Enter a `Name:` for the disk
|
||||
- If you are installing macOS Mojave or later (Catalina, Big Sur,
|
||||
Monterey, Ventura and Sonoma), choose any of the APFS options as
|
||||
the filesystem. MacOS Extended may not work.
|
||||
- Click **Erase**.
|
||||
- Click **Done**.
|
||||
- Close Disk Utility
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Reinstall macOS** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- On the first reboot use cursor keys and enter key to select **macOS
|
||||
Installer**
|
||||
- On the subsequent reboots use cursor keys and enter key to select
|
||||
the disk you named
|
||||
- Once you have finished installing macOS you will be presented with an
|
||||
the out-of-the-box first-start wizard to configure various options and
|
||||
set up your username and password
|
||||
- OPTIONAL: After you have concluded the out-of-the-box wizard, you may
|
||||
want to enable the TRIM feature that the computer industry created for
|
||||
SSD disks. This feature in our macOS installation will allow QuickEmu
|
||||
to compact (shrink) your macOS disk image whenever you delete files
|
||||
inside the Virtual Machine. Without this step your macOS disk image
|
||||
will only ever get larger and will not shrink even when you delete
|
||||
lots of data inside macOS.
|
||||
- To enable TRIM, open the Terminal application and type the following
|
||||
command followed by pressing <kbd>enter</kbd> to tell macos to use
|
||||
the TRIM command on the hard disk when files are deleted:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
sudo trimforce enable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will be prompted to enter your account's password to gain the
|
||||
privilege needed. Once you've entered your password and pressed
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> the command will request confirmation
|
||||
in the form of two questions that require you to type
|
||||
<kbd>y</kbd> (for a "yes" response) followed by
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> to confirm.
|
||||
You will be prompted to enter your account’s password to gain the
|
||||
privilege needed. Once you’ve entered your password and pressed
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> the command will request confirmation in the form of
|
||||
two questions that require you to type <kbd>y</kbd> (for a “yes”
|
||||
response) followed by <kbd>enter</kbd> to confirm.
|
||||
|
||||
If you press <kbd>enter</kbd> without first typing
|
||||
<kbd>y</kbd> the system will consider that a negative
|
||||
response as though you said "no":
|
||||
If you press <kbd>enter</kbd> without first typing <kbd>y</kbd> the
|
||||
system will consider that a negative response as though you said “no”:
|
||||
|
||||
``` plain
|
||||
IMPORTANT NOTICE: This tool force-enables TRIM for all relevant attached devices, even though such devices may not have been validated for data integrity while using TRIM. Use of this tool to enable TRIM may result in unintended data loss or data corruption. It should not be used in a commercial operating environment or with important data. Before using this tool, you should back up all of your data and regularly back up data while TRIM is enabled. This tool is provided on an "as is" basis. APPLE MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, REGARDING THIS TOOL OR ITS USE ALONE OR IN COMBINATION WITH YOUR DEVICES, SYSTEMS, OR SERVICES. BY USING THIS TOOL TO ENABLE TRIM, YOU AGREE THAT, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, USE OF THE TOOL IS AT YOUR SOLE RISK AND THAT THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO SATISFACTORY QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, ACCURACY AND EFFORT IS WITH YOU.
|
||||
Are you sure you with to proceed (y/N)?
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And a second confirmation once you've confirmed the previous one:
|
||||
And a second confirmation once you’ve confirmed the previous one:
|
||||
|
||||
``` plain
|
||||
Your system will immediately reboot when this is complete.
|
||||
|
|
@ -629,60 +630,59 @@ disk_img="macos-catalina/disk.qcow2"
|
|||
macos_release="catalina"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `guest_os="macos"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for macOS.
|
||||
- `macos_release="catalina"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for a
|
||||
particular macOS release.
|
||||
- For example VirtIO Network and Memory Ballooning are available
|
||||
in Big Sur and newer, but not previous releases.
|
||||
- And VirtIO Block Media (disks) are supported/stable in Catalina
|
||||
and newer.
|
||||
- `guest_os="macos"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for macOS.
|
||||
- `macos_release="catalina"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for a
|
||||
particular macOS release.
|
||||
- For example VirtIO Network and Memory Ballooning are available in
|
||||
Big Sur and newer, but not previous releases.
|
||||
- And VirtIO Block Media (disks) are supported/stable in Catalina and
|
||||
newer.
|
||||
|
||||
# macOS compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
There are some considerations when running macOS via Quickemu.
|
||||
|
||||
- Supported macOS releases:
|
||||
- High Sierra
|
||||
- Mojave
|
||||
- Catalina **(Recommended)**
|
||||
- Big Sur
|
||||
- Monterey
|
||||
- Ventura
|
||||
- Sonoma
|
||||
- `quickemu` will automatically download the required
|
||||
[OpenCore](https://github.com/acidanthera/OpenCorePkg) bootloader
|
||||
and OVMF firmware from [OSX-KVM](https://github.com/kholia/OSX-KVM).
|
||||
- Optimised by default, but no GPU acceleration is available.
|
||||
- Host CPU vendor is detected and guest CPU is optimised
|
||||
accordingly.
|
||||
- [VirtIO Block
|
||||
Media](https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2019/06/macos-qemu-guest/) is
|
||||
used for the system disk where supported.
|
||||
- [VirtIO `usb-tablet`](http://philjordan.eu/osx-virt/) is used
|
||||
for the mouse.
|
||||
- VirtIO Network (`virtio-net`) is supported and enabled on macOS
|
||||
Big Sur and newer, but earlier releases use `vmxnet3`.
|
||||
- VirtIO Memory Ballooning is supported and enabled on macOS Big
|
||||
Sur and newer but disabled for other support macOS releases.
|
||||
- USB host and SPICE pass-through is:
|
||||
- UHCI (USB 2.0) on macOS Catalina and earlier.
|
||||
- XHCI (USB 3.0) on macOS Big Sur and newer.
|
||||
- Display resolution can only be changed via macOS System Preferences.
|
||||
- **Full Duplex audio requires [VoodooHDA
|
||||
OC](https://github.com/chris1111/VoodooHDA-OC) or pass-through a USB
|
||||
audio-device to the macOS guest VM**.
|
||||
- NOTE! [Gatekeeper](https://disable-gatekeeper.github.io/) and
|
||||
[System Integrity Protection
|
||||
(SIP)](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/security/disabling_and_enabling_system_integrity_protection)
|
||||
need to be disabled to install VoodooHDA OC
|
||||
- File sharing between guest and host is available via
|
||||
[virtio-9p](https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9psetup) and [SPICE
|
||||
webdavd](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/phodav/-/merge_requests/24).
|
||||
- Copy/paste via SPICE agent is **not available on macOS**.
|
||||
- Supported macOS releases:
|
||||
- High Sierra
|
||||
- Mojave
|
||||
- Catalina **(Recommended)**
|
||||
- Big Sur
|
||||
- Monterey
|
||||
- Ventura
|
||||
- Sonoma
|
||||
- `quickemu` will automatically download the required
|
||||
[OpenCore](https://github.com/acidanthera/OpenCorePkg) bootloader and
|
||||
OVMF firmware from [OSX-KVM](https://github.com/kholia/OSX-KVM).
|
||||
- Optimised by default, but no GPU acceleration is available.
|
||||
- Host CPU vendor is detected and guest CPU is optimised accordingly.
|
||||
- [VirtIO Block
|
||||
Media](https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2019/06/macos-qemu-guest/) is
|
||||
used for the system disk where supported.
|
||||
- [VirtIO `usb-tablet`](http://philjordan.eu/osx-virt/) is used for
|
||||
the mouse.
|
||||
- VirtIO Network (`virtio-net`) is supported and enabled on macOS Big
|
||||
Sur and newer, but earlier releases use `vmxnet3`.
|
||||
- VirtIO Memory Ballooning is supported and enabled on macOS Big Sur
|
||||
and newer but disabled for other support macOS releases.
|
||||
- USB host and SPICE pass-through is:
|
||||
- UHCI (USB 2.0) on macOS Catalina and earlier.
|
||||
- XHCI (USB 3.0) on macOS Big Sur and newer.
|
||||
- Display resolution can only be changed via macOS System Preferences.
|
||||
- **Full Duplex audio requires [VoodooHDA
|
||||
OC](https://github.com/chris1111/VoodooHDA-OC) or pass-through a USB
|
||||
audio-device to the macOS guest VM**.
|
||||
- NOTE! [Gatekeeper](https://disable-gatekeeper.github.io/) and
|
||||
[System Integrity Protection
|
||||
(SIP)](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/security/disabling_and_enabling_system_integrity_protection)
|
||||
need to be disabled to install VoodooHDA OC
|
||||
- File sharing between guest and host is available via
|
||||
[virtio-9p](https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9psetup) and [SPICE
|
||||
webdavd](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/phodav/-/merge_requests/24).
|
||||
- Copy/paste via SPICE agent is **not available on macOS**.
|
||||
|
||||
# macOS App Store
|
||||
|
||||
If you see *"Your device or computer could not be verified"* when you
|
||||
If you see *“Your device or computer could not be verified”* when you
|
||||
try to login to the App Store, make sure that your wired ethernet device
|
||||
is `en0`. Use `ifconfig` in a terminal to verify this.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -709,7 +709,7 @@ automatically and create an optimised virtual machine configuration.
|
|||
This configuration also includes the [VirtIO drivers for
|
||||
Windows](https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/).
|
||||
|
||||
**Windows 8.1** is also supported but doesn't feature any automated
|
||||
**Windows 8.1** is also supported but doesn’t feature any automated
|
||||
installation or driver optimisation.
|
||||
|
||||
`quickget` can also download [Windows 10
|
||||
|
|
@ -727,12 +727,12 @@ quickget windows 11
|
|||
quickemu --vm windows-11.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- All relevant drivers and services should be installed automatically.
|
||||
- A local administrator user account is automatically created, with
|
||||
these credentials:
|
||||
- Username: `Quickemu`
|
||||
- Password: `quickemu`
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- All relevant drivers and services should be installed automatically.
|
||||
- A local administrator user account is automatically created, with
|
||||
these credentials:
|
||||
- Username: `Quickemu`
|
||||
- Password: `quickemu`
|
||||
|
||||
Further information is available from the project
|
||||
[wiki](https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickemu/wiki/04-Create-Windows-virtual-machines)
|
||||
|
|
@ -749,7 +749,7 @@ Arguments
|
|||
--access : Enable remote spice access support. 'local' (default), 'remote', 'clientipaddress'
|
||||
--braille : Enable braille support. Requires SDL.
|
||||
--delete-disk : Delete the disk image and EFI variables
|
||||
--delete-vm : Delete the entire VM and it's configuration
|
||||
--delete-vm : Delete the entire VM and its configuration
|
||||
--display : Select display backend. 'sdl' (default), 'gtk', 'none', 'spice' or 'spice-app'
|
||||
--fullscreen : Starts VM in full screen mode (Ctl+Alt+f to exit)
|
||||
--ignore-msrs-always : Configure KVM to always ignore unhandled machine-specific registers
|
||||
|
|
@ -793,93 +793,42 @@ shortcut.
|
|||
quickemu --vm ubuntu-22.04-desktop.conf --shortcut
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Screen and window size (Linux guests only)
|
||||
|
||||
`qemu` will always default to the primary monitor to display the VM's
|
||||
window.
|
||||
|
||||
Without the `--screen` option, `quickemu` will look for the size of the
|
||||
smallest monitor, and use a size that fits on said monitor.
|
||||
|
||||
The `--screen` option forces `quickemu` to use the size of the given
|
||||
monitor to compute the size of the window. **It won't use that monitor
|
||||
to display the VM's window if it's not the primary monitor**. This is
|
||||
useful if the primary monitor if not the smallest one, and if the VM's
|
||||
window doesn't need to be moved around.
|
||||
|
||||
The `--screen` option is also useful with the `--fullscreen` option,
|
||||
again because `qemu` will always use the primary monitor. In order for
|
||||
the fullscreen mode to work properly, the resolution of the VM's window
|
||||
must match the resolution of the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
To know which screen to use, type:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
xrandr --listmonitors | grep -v Monitors
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The command will output something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
0: +*HDMI-0 2560/597x1440/336+1920+0 HDMI-0
|
||||
1: +DVI-D-0 1920/527x1080/296+0+0 DVI-D-0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The first number is what needs to be passed to the `--screen` option.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
quickemu --vm vm.conf --screen 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above uses the 2560x1440 screen to compute the size of the window,
|
||||
which Quickemu sizes to 2048x1152. Without the `--screen` option,
|
||||
Quickemu would have used the 1920x1080 monitor which results in a window
|
||||
size of 1664x936.
|
||||
|
||||
The '--screenpct' is an optional integer value between 25 \<= pct \< 100
|
||||
which will override system default screen sizes. The VM size will be
|
||||
'pct' of the chosen screen. **If --fullscreen is chosen screen will be
|
||||
fullsize instead of being scaled down by --screenpct value.**
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
Useful reference that assisted the development of Quickemu.
|
||||
|
||||
- General
|
||||
- [QEMU's documentation!](https://qemu.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
|
||||
- <https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Qemu/KVM_Virtual_Machines>
|
||||
- <https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2020/01/qemu-sound-audiodev/>
|
||||
- macOS
|
||||
- <https://www.nicksherlock.com/2020/06/installing-macos-big-sur-on-proxmox/>
|
||||
- <https://passthroughpo.st/mac-os-adds-early-support-for-virtio-qemu/>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/kholia/OSX-KVM>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/thenickdude/KVM-Opencore>
|
||||
- <https://gist.github.com/MCJack123/943eaca762730ca4b7ae460b731b68e7>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/acidanthera/OpenCorePkg/tree/master/Utilities/macrecovery>
|
||||
- <https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2017/09/running-macos-as-guest-in-kvm/>
|
||||
- <https://www.nicksherlock.com/2017/10/passthrough-of-advanced-cpu-features-for-macos-high-sierra-guests/>
|
||||
- <http://philjordan.eu/osx-virt/>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/Dids/clover-builder>
|
||||
- [OpenCore
|
||||
Configurator](https://mackie100projects.altervista.org)
|
||||
- Windows
|
||||
- <https://www.heiko-sieger.info/running-windows-10-on-linux-using-kvm-with-vga-passthrough/>
|
||||
- <https://leduccc.medium.com/improving-the-performance-of-a-windows-10-guest-on-qemu-a5b3f54d9cf5>
|
||||
- <https://frontpagelinux.com/tutorials/how-to-use-linux-kvm-to-optimize-your-windows-10-virtual-machine/>
|
||||
- <https://turlucode.com/qemu-command-line-args/>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/pbatard/Fido>
|
||||
- <https://www.catapultsystems.com/blogs/create-zero-touch-windows-10-iso/>
|
||||
- TPM
|
||||
- <https://qemu-project.gitlab.io/qemu/specs/tpm.html>
|
||||
- <https://www.tecklyfe.com/how-to-create-a-windows-11-virtual-machine-in-qemu/>
|
||||
- 9p & virtiofs
|
||||
- <https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9p>
|
||||
- <https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9psetup>
|
||||
- <https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2019/06/macos-qemu-guest/>
|
||||
- <https://superuser.com/questions/628169/how-to-share-a-directory-with-the-host-without-networking-in-qemu>
|
||||
- <https://virtio-fs.gitlab.io/>
|
||||
- General
|
||||
- [QEMU’s documentation!](https://qemu.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
|
||||
- <https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Qemu/KVM_Virtual_Machines>
|
||||
- <https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2020/01/qemu-sound-audiodev/>
|
||||
- macOS
|
||||
- <https://www.nicksherlock.com/2020/06/installing-macos-big-sur-on-proxmox/>
|
||||
- <https://passthroughpo.st/mac-os-adds-early-support-for-virtio-qemu/>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/kholia/OSX-KVM>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/thenickdude/KVM-Opencore>
|
||||
- <https://gist.github.com/MCJack123/943eaca762730ca4b7ae460b731b68e7>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/acidanthera/OpenCorePkg/tree/master/Utilities/macrecovery>
|
||||
- <https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2017/09/running-macos-as-guest-in-kvm/>
|
||||
- <https://www.nicksherlock.com/2017/10/passthrough-of-advanced-cpu-features-for-macos-high-sierra-guests/>
|
||||
- <http://philjordan.eu/osx-virt/>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/Dids/clover-builder>
|
||||
- [OpenCore Configurator](https://mackie100projects.altervista.org)
|
||||
- Windows
|
||||
- <https://www.heiko-sieger.info/running-windows-10-on-linux-using-kvm-with-vga-passthrough/>
|
||||
- <https://leduccc.medium.com/improving-the-performance-of-a-windows-10-guest-on-qemu-a5b3f54d9cf5>
|
||||
- <https://frontpagelinux.com/tutorials/how-to-use-linux-kvm-to-optimize-your-windows-10-virtual-machine/>
|
||||
- <https://turlucode.com/qemu-command-line-args/>
|
||||
- <https://github.com/pbatard/Fido>
|
||||
- <https://www.catapultsystems.com/blogs/create-zero-touch-windows-10-iso/>
|
||||
- TPM
|
||||
- <https://qemu-project.gitlab.io/qemu/specs/tpm.html>
|
||||
- <https://www.tecklyfe.com/how-to-create-a-windows-11-virtual-machine-in-qemu/>
|
||||
- 9p & virtiofs
|
||||
- <https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9p>
|
||||
- <https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9psetup>
|
||||
- <https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2019/06/macos-qemu-guest/>
|
||||
- <https://superuser.com/questions/628169/how-to-share-a-directory-with-the-host-without-networking-in-qemu>
|
||||
- <https://virtio-fs.gitlab.io/>
|
||||
|
||||
# AUTHORS
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -82,13 +82,13 @@ disk_img="macos-catalina/disk.qcow2"
|
|||
macos_release="catalina"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `guest_os="macos"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for macOS.
|
||||
- `macos_release="catalina"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for a
|
||||
particular macOS release.
|
||||
- For example VirtIO Network and Memory Ballooning are available
|
||||
in Big Sur and newer, but not previous releases.
|
||||
- And VirtIO Block Media (disks) are supported/stable in Catalina
|
||||
and newer.
|
||||
- `guest_os="macos"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for macOS.
|
||||
- `macos_release="catalina"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for a
|
||||
particular macOS release.
|
||||
- For example VirtIO Network and Memory Ballooning are available in
|
||||
Big Sur and newer, but not previous releases.
|
||||
- And VirtIO Block Media (disks) are supported/stable in Catalina and
|
||||
newer.
|
||||
|
||||
The default Windows 11 configuration looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -101,10 +101,10 @@ tpm="on"
|
|||
secureboot="on"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `guest_os="windows"` instructs `quickemu` to optimise for Windows.
|
||||
- `fixed_iso=` specifies the ISO image that provides VirtIO drivers.
|
||||
- `tpm="on"` instructs `quickemu` to create a software emulated TPM
|
||||
device using `swtpm`.
|
||||
- `guest_os="windows"` instructs `quickemu` to optimise for Windows.
|
||||
- `fixed_iso=` specifies the ISO image that provides VirtIO drivers.
|
||||
- `tpm="on"` instructs `quickemu` to create a software emulated TPM
|
||||
device using `swtpm`.
|
||||
|
||||
### BIOS and EFI
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ Since Quickemu 2.1.0 `efi` is the default boot option. If you want to
|
|||
override this behaviour then add the following line to you VM
|
||||
configuration to enable legacy BIOS.
|
||||
|
||||
- `boot="legacy"` - Enable Legacy BIOS boot
|
||||
- `boot="legacy"` - Enable Legacy BIOS boot
|
||||
|
||||
### Tuning CPU cores, RAM & disks
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -123,11 +123,10 @@ your liking.
|
|||
|
||||
Add additional lines to your virtual machine configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
- `cpu_cores="4"` - Specify the number of CPU cores allocated to the
|
||||
VM
|
||||
- `ram="4G"` - Specify the amount of RAM to allocate to the VM
|
||||
- `disk_size="16G"` - Specify the size of the virtual disk allocated
|
||||
to the VM
|
||||
- `cpu_cores="4"` - Specify the number of CPU cores allocated to the VM
|
||||
- `ram="4G"` - Specify the amount of RAM to allocate to the VM
|
||||
- `disk_size="16G"` - Specify the size of the virtual disk allocated to
|
||||
the VM
|
||||
|
||||
### Disk preallocation
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -139,22 +138,22 @@ Specify what disk preallocation should be used, if any, when creating
|
|||
the system disk image by adding a line like this to your VM
|
||||
configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
- `preallocation="metadata"`
|
||||
- `preallocation="metadata"`
|
||||
|
||||
### CD-ROM disks
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to expose an ISO image from the host to guest add the
|
||||
following line to the VM configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
- `fixed_iso="/path/to/image.iso"`
|
||||
- `fixed_iso="/path/to/image.iso"`
|
||||
|
||||
### Floppy disks
|
||||
|
||||
If you're like [Alan Pope](https://popey.com) you'll probably want to
|
||||
If you’re like [Alan Pope](https://popey.com) you’ll probably want to
|
||||
mount a floppy disk image in the guest. To do so add the following line
|
||||
to the VM configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
- `floppy="/path/to/floppy.img"`
|
||||
- `floppy="/path/to/floppy.img"`
|
||||
|
||||
### File Sharing
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -178,17 +177,17 @@ when the virtual machine is started. For example:
|
|||
|
||||
- smbd: On guest: smb://10.0.2.4/qemu
|
||||
|
||||
If using a Windows guest, right-click on "This PC", click "Add a network
|
||||
location", and paste this address, removing `smb:` and replacing forward
|
||||
If using a Windows guest, right-click on “This PC”, click “Add a network
|
||||
location”, and paste this address, removing `smb:` and replacing forward
|
||||
slashes with backslashes (in this example `\\10.0.2.4\qemu`).
|
||||
|
||||
#### SPICE WebDAV 🐧 🪟
|
||||
|
||||
- TBD
|
||||
- TBD
|
||||
|
||||
#### VirtIO-9P 🐧 🍏
|
||||
|
||||
- TBD
|
||||
- TBD
|
||||
|
||||
### Networking
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -197,19 +196,19 @@ slashes with backslashes (in this example `\\10.0.2.4\qemu`).
|
|||
Add an additional line to your virtual machine configuration. For
|
||||
example:
|
||||
|
||||
- `port_forwards=("8123:8123" "8888:80")`
|
||||
- `port_forwards=("8123:8123" "8888:80")`
|
||||
|
||||
In the example above:
|
||||
|
||||
- Port 8123 on the host is forwarded to port 8123 on the guest.
|
||||
- Port 8888 on the host is forwarded to port 80 on the guest.
|
||||
- Port 8123 on the host is forwarded to port 8123 on the guest.
|
||||
- Port 8888 on the host is forwarded to port 80 on the guest.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Disable networking
|
||||
|
||||
To completely disable all network interfaces in a guest VM add this
|
||||
additional line to your virtual machine configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
- `network="none"`
|
||||
- `network="none"`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Restricted networking
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,14 +220,14 @@ This can be used to prevent software running inside the guest from
|
|||
phoning home while still providing a network inside the guest. Add this
|
||||
additional line to your virtual machine configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
- `network="restrict"`
|
||||
- `network="restrict"`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Bridged networking
|
||||
|
||||
Connect your virtual machine to a preconfigured network bridge. Add an
|
||||
additional line to your virtual machine configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
- `network="br0"`
|
||||
- `network="br0"`
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to have a persistent MAC address for your bridged network
|
||||
interface in the guest VM you can add `macaddr` to the virtual machine
|
||||
|
|
@ -237,7 +236,7 @@ configuration. QEMU requires that the MAC address is in the range:
|
|||
|
||||
So you can generate your own MAC addresses with:
|
||||
|
||||
- `macaddr="52:54:00:AB:51:AE"`
|
||||
- `macaddr="52:54:00:AB:51:AE"`
|
||||
|
||||
### USB redirection
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -246,12 +245,12 @@ pass-through.
|
|||
|
||||
#### SPICE redirection (recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
Using SPICE for USB pass-through is easiest as it doesn't require any
|
||||
Using SPICE for USB pass-through is easiest as it doesn’t require any
|
||||
elevated permission:
|
||||
|
||||
- Start Quickemu with `--display spice` and then
|
||||
- select `Input` -\> `Select USB Device for redirection` from the menu
|
||||
to choose which device(s) you want to attach to the guest.
|
||||
- Start Quickemu with `--display spice` and then
|
||||
- select `Input` -\> `Select USB Device for redirection` from the menu
|
||||
to choose which device(s) you want to attach to the guest.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Enabling SPICE redirection on NixOS
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -275,14 +274,14 @@ preferred, see above.
|
|||
Add an additional line to your virtual machine configuration. For
|
||||
example:
|
||||
|
||||
- `usb_devices=("046d:082d" "046d:085e")`
|
||||
- `usb_devices=("046d:082d" "046d:085e")`
|
||||
|
||||
In the example above:
|
||||
|
||||
- The USB device with vendor_id 046d and product_id 082d will be
|
||||
exposed to the guest.
|
||||
- The USB device with vendor_id 046d and product_id 085e will be
|
||||
exposed to the guest.
|
||||
- The USB device with vendor_id 046d and product_id 082d will be exposed
|
||||
to the guest.
|
||||
- The USB device with vendor_id 046d and product_id 085e will be exposed
|
||||
to the guest.
|
||||
|
||||
If the USB devices are not writable, `quickemu` will display the
|
||||
appropriate commands to modify the USB device(s) access permissions,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,26 +11,44 @@ quickget \- download and prepare materials for building a quickemu VM
|
|||
configuration for \f[CR]quickemu\f[R] to use to build and run
|
||||
.SH OPTIONS
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]version | \-version | \[en]version\f[R]
|
||||
show version (from Quickemu)
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]list | list_csv | list_json\f[R]
|
||||
provide a csv list of all supported guest OSes, versions and variants.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\f[CB]\-\-show\-iso\-url\f[B] | \-s\f[R] {\f[B]os\f[R]} {\f[B]release\f[R]} [\f[B]edition\f[R]]
|
||||
show ISO download URL
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\f[CB]\-\-test\-iso\-url\f[B] | \-t\f[R] {\f[B]os\f[R]} {\f[B]release\f[R]} [\f[B]edition\f[R]]
|
||||
test if ISO is available
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\f[CB]\-\-open\-distro\-homepage\f[B] | \-o\f[R] {\f[B]os\f[R]}
|
||||
open OS homepage in browser
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B][OS] [Release] [Edition]\f[R]
|
||||
specify the OS and release (and optional edition) if insufficient input
|
||||
is provided a list of missing options will be reported and the script
|
||||
will exit.
|
||||
Editions may not apply and will be defaulted if not provided.
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-download\f[R] [edition]
|
||||
Download image; no VM configuration
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-create\-config\f[R] [path/url]
|
||||
Create VM config for a OS image
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-open\-homepage\f[R]
|
||||
Open homepage for the OS
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-show\f[R] [os]
|
||||
Show OS information
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-url\f[R] [os] [release] [edition]
|
||||
Show image URL(s)
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-check\f[R] [os] [release] [edition]
|
||||
Check image URL(s)
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-list\f[R]
|
||||
List all supported systems
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-list\-csv\f[R]
|
||||
List everything in csv format
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-list\-json\f[R]
|
||||
List everything in json format
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-version\f[R]
|
||||
Show version
|
||||
.TP
|
||||
\f[B]\-\-help\f[R]
|
||||
Show this help message
|
||||
.SH NOTES
|
||||
.SS Creating Linux guests 🐧
|
||||
.SS Ubuntu
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,28 +22,45 @@ configuration for `quickemu` to use to build and run
|
|||
|
||||
# OPTIONS
|
||||
|
||||
**version \| -version \| --version**
|
||||
: show version (from Quickemu)
|
||||
|
||||
**list \| list_csv \| list_json**
|
||||
: provide a csv list of all supported guest OSes, versions and
|
||||
variants.
|
||||
|
||||
**`--show-iso-url` \| -s** {**os**} {**release**} \[**edition**\]
|
||||
: show ISO download URL
|
||||
|
||||
**`--test-iso-url` \| -t** {**os**} {**release**} \[**edition**\]
|
||||
: test if ISO is available
|
||||
|
||||
**`--open-distro-homepage` \| -o** {**os**}
|
||||
: open OS homepage in browser
|
||||
|
||||
**\[OS\] \[Release\] \[Edition\]**
|
||||
: specify the OS and release (and optional edition) if insufficient
|
||||
input is provided a list of missing options will be reported and the
|
||||
script will exit. Editions may not apply and will be defaulted if
|
||||
not provided.
|
||||
|
||||
**--download** <os> <release> \[edition\]
|
||||
: Download image; no VM configuration
|
||||
|
||||
**--create-config** <os> \[path/url\]
|
||||
: Create VM config for a OS image
|
||||
|
||||
**--open-homepage** <os>
|
||||
: Open homepage for the OS
|
||||
|
||||
**--show** \[os\]
|
||||
: Show OS information
|
||||
|
||||
**--url** \[os\] \[release\] \[edition\]
|
||||
: Show image URL(s)
|
||||
|
||||
**--check** \[os\] \[release\] \[edition\]
|
||||
: Check image URL(s)
|
||||
|
||||
**--list**
|
||||
: List all supported systems
|
||||
|
||||
**--list-csv**
|
||||
: List everything in csv format
|
||||
|
||||
**--list-json**
|
||||
: List everything in json format
|
||||
|
||||
**--version**
|
||||
: Show version
|
||||
|
||||
**--help**
|
||||
: Show this help message
|
||||
|
||||
# NOTES
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating Linux guests 🐧
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,14 +75,14 @@ quickget ubuntu 22.04
|
|||
quickemu --vm ubuntu-22.04.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-vdagent`
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-webdavd`
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-vdagent`
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
- `sudo apt install spice-webdavd`
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu daily-live images
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,18 +107,18 @@ The project
|
|||
[wiki](https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickemu/wiki/02-Create-Linux-virtual-machines)
|
||||
may have further information.
|
||||
|
||||
- `edubuntu` (Edubuntu)
|
||||
- `kubuntu` (Kubuntu)
|
||||
- `lubuntu` (Lubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-budgie` (Ubuntu Budgie)
|
||||
- `ubuntucinnamon` (Ubuntu Cinnamon)
|
||||
- `ubuntukylin` (Ubuntu Kylin)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-mate` (Ubuntu MATE)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-server` (Ubuntu Server)
|
||||
- `ubuntustudio` (Ubuntu Studio)
|
||||
- `ubuntu` (Ubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-unity` (Ubuntu Unity)
|
||||
- `xubuntu` (Xubuntu)
|
||||
- `edubuntu` (Edubuntu)
|
||||
- `kubuntu` (Kubuntu)
|
||||
- `lubuntu` (Lubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-budgie` (Ubuntu Budgie)
|
||||
- `ubuntucinnamon` (Ubuntu Cinnamon)
|
||||
- `ubuntukylin` (Ubuntu Kylin)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-mate` (Ubuntu MATE)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-server` (Ubuntu Server)
|
||||
- `ubuntustudio` (Ubuntu Studio)
|
||||
- `ubuntu` (Ubuntu)
|
||||
- `ubuntu-unity` (Ubuntu Unity)
|
||||
- `xubuntu` (Xubuntu)
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use `quickget` with advanced options :
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,96 +159,96 @@ Further information is available from the project
|
|||
|
||||
`quickget` also supports:
|
||||
|
||||
- `alma` (AlmaLinux)
|
||||
- `alpine` (Alpine Linux)
|
||||
- `android` (Android x86)
|
||||
- `antix` (Antix)
|
||||
- `archcraft` (Archcraft)
|
||||
- `archlinux` (Arch Linux)
|
||||
- `arcolinux` (Arco Linux)
|
||||
- `artixlinux` (Artix Linux)
|
||||
- `athenaos` (Athena OS)
|
||||
- `batocera` (Batocera)
|
||||
- `bazzite` (Bazzite)
|
||||
- `biglinux` (BigLinux)
|
||||
- `blendos` (BlendOS)
|
||||
- `bodhi` (Bodhi)
|
||||
- `bunsenlabs` (BunsenLabs)
|
||||
- `cachyos` (CachyOS)
|
||||
- `centos-stream` (CentOS Stream)
|
||||
- `chimeralinux` (Chimera Linux)
|
||||
- `crunchbang++` (Crunchbangplusplus)
|
||||
- `debian` (Debian)
|
||||
- `deepin` (Deepin)
|
||||
- `devuan` (Devuan)
|
||||
- `dragonflybsd` (DragonFlyBSD)
|
||||
- `easyos` (EasyOS)
|
||||
- `elementary` (elementary OS)
|
||||
- `endeavouros` (EndeavourOS)
|
||||
- `endless` (Endless OS)
|
||||
- `fedora` (Fedora)
|
||||
- `freebsd` (FreeBSD)
|
||||
- `freedos` (FreeDOS)
|
||||
- `garuda` (Garuda Linux)
|
||||
- `gentoo` (Gentoo)
|
||||
- `ghostbsd` (GhostBSD)
|
||||
- `gnomeos` (GNOME OS)
|
||||
- `guix` (Guix)
|
||||
- `haiku` (Haiku)
|
||||
- `holoiso` (HoloISO)
|
||||
- `kali` (Kali)
|
||||
- `kdeneon` (KDE Neon)
|
||||
- `kolibrios` (KolibriOS)
|
||||
- `linuxlite` (Linux Lite)
|
||||
- `linuxmint` (Linux Mint)
|
||||
- `lmde` (Linux Mint Debian Edition)
|
||||
- `mageia` (Mageia)
|
||||
- `manjaro` (Manjaro)
|
||||
- `mxlinux` (MX Linux)
|
||||
- `netboot` (netboot.xyz)
|
||||
- `netbsd` (NetBSD)
|
||||
- `nitrux` (Nitrux)
|
||||
- `nixos` (NixOS)
|
||||
- `nwg-shell` (nwg-shell)
|
||||
- `openbsd` (OpenBSD)
|
||||
- `openindiana` (OpenIndiana)
|
||||
- `opensuse` (openSUSE)
|
||||
- `oraclelinux` (Oracle Linux)
|
||||
- `parrotsec` (Parrot Security)
|
||||
- `peppermint` (PeppermintOS)
|
||||
- `popos` (Pop!\_OS)
|
||||
- `porteus` (Porteus)
|
||||
- `primtux` (PrimTux)
|
||||
- `pureos` (PureOS)
|
||||
- `reactos` (ReactOS)
|
||||
- `rebornos` (RebornOS)
|
||||
- `rockylinux` (Rocky Linux)
|
||||
- `siduction` (Siduction)
|
||||
- `slackware` (Slackware)
|
||||
- `slax` (Slax)
|
||||
- `slint` (Slint)
|
||||
- `slitaz` (SliTaz)
|
||||
- `solus` (Solus)
|
||||
- `sparkylinux` (SparkyLinux)
|
||||
- `spirallinux` (SpiralLinux)
|
||||
- `tails` (Tails)
|
||||
- `tinycore` (Tiny Core Linux)
|
||||
- `trisquel` (Trisquel-)
|
||||
- `truenas-core` (TrueNAS Core)
|
||||
- `truenas-scale` (TrueNAS Scale)
|
||||
- `tuxedo-os` (Tuxedo OS)
|
||||
- `vanillaos` (Vanilla OS)
|
||||
- `void` (Void Linux)
|
||||
- `vxlinux` (VX Linux)
|
||||
- `zorin` (Zorin OS)
|
||||
- `alma` (AlmaLinux)
|
||||
- `alpine` (Alpine Linux)
|
||||
- `android` (Android x86)
|
||||
- `antix` (Antix)
|
||||
- `archcraft` (Archcraft)
|
||||
- `archlinux` (Arch Linux)
|
||||
- `arcolinux` (Arco Linux)
|
||||
- `artixlinux` (Artix Linux)
|
||||
- `athenaos` (Athena OS)
|
||||
- `batocera` (Batocera)
|
||||
- `bazzite` (Bazzite)
|
||||
- `biglinux` (BigLinux)
|
||||
- `blendos` (BlendOS)
|
||||
- `bodhi` (Bodhi)
|
||||
- `bunsenlabs` (BunsenLabs)
|
||||
- `cachyos` (CachyOS)
|
||||
- `centos-stream` (CentOS Stream)
|
||||
- `chimeralinux` (Chimera Linux)
|
||||
- `crunchbang++` (Crunchbangplusplus)
|
||||
- `debian` (Debian)
|
||||
- `deepin` (Deepin)
|
||||
- `devuan` (Devuan)
|
||||
- `dragonflybsd` (DragonFlyBSD)
|
||||
- `easyos` (EasyOS)
|
||||
- `elementary` (elementary OS)
|
||||
- `endeavouros` (EndeavourOS)
|
||||
- `endless` (Endless OS)
|
||||
- `fedora` (Fedora)
|
||||
- `freebsd` (FreeBSD)
|
||||
- `freedos` (FreeDOS)
|
||||
- `garuda` (Garuda Linux)
|
||||
- `gentoo` (Gentoo)
|
||||
- `ghostbsd` (GhostBSD)
|
||||
- `gnomeos` (GNOME OS)
|
||||
- `guix` (Guix)
|
||||
- `haiku` (Haiku)
|
||||
- `holoiso` (HoloISO)
|
||||
- `kali` (Kali)
|
||||
- `kdeneon` (KDE Neon)
|
||||
- `kolibrios` (KolibriOS)
|
||||
- `linuxlite` (Linux Lite)
|
||||
- `linuxmint` (Linux Mint)
|
||||
- `lmde` (Linux Mint Debian Edition)
|
||||
- `mageia` (Mageia)
|
||||
- `manjaro` (Manjaro)
|
||||
- `mxlinux` (MX Linux)
|
||||
- `netboot` (netboot.xyz)
|
||||
- `netbsd` (NetBSD)
|
||||
- `nitrux` (Nitrux)
|
||||
- `nixos` (NixOS)
|
||||
- `nwg-shell` (nwg-shell)
|
||||
- `openbsd` (OpenBSD)
|
||||
- `openindiana` (OpenIndiana)
|
||||
- `opensuse` (openSUSE)
|
||||
- `oraclelinux` (Oracle Linux)
|
||||
- `parrotsec` (Parrot Security)
|
||||
- `peppermint` (PeppermintOS)
|
||||
- `popos` (Pop!\_OS)
|
||||
- `porteus` (Porteus)
|
||||
- `primtux` (PrimTux)
|
||||
- `pureos` (PureOS)
|
||||
- `reactos` (ReactOS)
|
||||
- `rebornos` (RebornOS)
|
||||
- `rockylinux` (Rocky Linux)
|
||||
- `siduction` (Siduction)
|
||||
- `slackware` (Slackware)
|
||||
- `slax` (Slax)
|
||||
- `slint` (Slint)
|
||||
- `slitaz` (SliTaz)
|
||||
- `solus` (Solus)
|
||||
- `sparkylinux` (SparkyLinux)
|
||||
- `spirallinux` (SpiralLinux)
|
||||
- `tails` (Tails)
|
||||
- `tinycore` (Tiny Core Linux)
|
||||
- `trisquel` (Trisquel-)
|
||||
- `truenas-core` (TrueNAS Core)
|
||||
- `truenas-scale` (TrueNAS Scale)
|
||||
- `tuxedo-os` (Tuxedo OS)
|
||||
- `vanillaos` (Vanilla OS)
|
||||
- `void` (Void Linux)
|
||||
- `vxlinux` (VX Linux)
|
||||
- `zorin` (Zorin OS)
|
||||
|
||||
### [Custom Linux guests](https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickemu/wiki/02-Create-Linux-virtual-machines#manually-create-linux-guests)
|
||||
|
||||
Or you can download a Linux image and manually create a VM
|
||||
configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
- Download a .iso image of a Linux distribution
|
||||
- Create a VM configuration file; for example `debian-bullseye.conf`
|
||||
- Download a .iso image of a Linux distribution
|
||||
- Create a VM configuration file; for example `debian-bullseye.conf`
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
guest_os="linux"
|
||||
|
|
@ -239,18 +256,18 @@ disk_img="debian-bullseye/disk.qcow2"
|
|||
iso="debian-bullseye/firmware-11.0.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `quickemu` to start the virtual machine:
|
||||
- Use `quickemu` to start the virtual machine:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
quickemu --vm debian-bullseye.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection.
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
- Complete the installation as normal.
|
||||
- Post-install:
|
||||
- Install the SPICE agent (`spice-vdagent`) in the guest to enable
|
||||
copy/paste and USB redirection.
|
||||
- Install the SPICE WebDAV agent (`spice-webdavd`) in the guest to
|
||||
enable file sharing.
|
||||
|
||||
## Supporting old Linux distros
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -276,62 +293,59 @@ quickemu --vm macos-catalina.conf
|
|||
macOS `mojave`, `catalina`, `big-sur`, `monterey`, `ventura` and
|
||||
`sonoma` are supported.
|
||||
|
||||
- Use cursor keys and enter key to select the **macOS Base System**
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Disk Utility** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Select `QEMU HARDDISK Media` (\~103.08GB) from the list (on
|
||||
Big Sur and above use `Apple Inc. VirtIO Block Device`) and
|
||||
click **Erase**.
|
||||
- Enter a `Name:` for the disk
|
||||
- If you are installing macOS Mojave or later (Catalina, Big
|
||||
Sur, Monterey, Ventura and Sonoma), choose any of the APFS
|
||||
options as the filesystem. MacOS Extended may not work.
|
||||
- Click **Erase**.
|
||||
- Click **Done**.
|
||||
- Close Disk Utility
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Reinstall macOS** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- On the first reboot use cursor keys and enter key to select
|
||||
**macOS Installer**
|
||||
- On the subsequent reboots use cursor keys and enter key to
|
||||
select the disk you named
|
||||
- Once you have finished installing macOS you will be presented with
|
||||
an the out-of-the-box first-start wizard to configure various
|
||||
options and set up your username and password
|
||||
- OPTIONAL: After you have concluded the out-of-the-box wizard, you
|
||||
may want to enable the TRIM feature that the computer industry
|
||||
created for SSD disks. This feature in our macOS installation will
|
||||
allow QuickEmu to compact (shrink) your macOS disk image whenever
|
||||
you delete files inside the Virtual Machine. Without this step your
|
||||
macOS disk image will only ever get larger and will not shrink even
|
||||
when you delete lots of data inside macOS.
|
||||
- To enable TRIM, open the Terminal application and type the
|
||||
following command followed by pressing
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> to tell macos to use the TRIM
|
||||
command on the hard disk when files are deleted:
|
||||
- Use cursor keys and enter key to select the **macOS Base System**
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Disk Utility** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Select `QEMU HARDDISK Media` (~103.08GB) from the list (on Big Sur
|
||||
and above use `Apple Inc. VirtIO Block Device`) and click
|
||||
**Erase**.
|
||||
- Enter a `Name:` for the disk
|
||||
- If you are installing macOS Mojave or later (Catalina, Big Sur,
|
||||
Monterey, Ventura and Sonoma), choose any of the APFS options as
|
||||
the filesystem. MacOS Extended may not work.
|
||||
- Click **Erase**.
|
||||
- Click **Done**.
|
||||
- Close Disk Utility
|
||||
- From **macOS Utilities**
|
||||
- Click **Reinstall macOS** and **Continue**
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- On the first reboot use cursor keys and enter key to select **macOS
|
||||
Installer**
|
||||
- On the subsequent reboots use cursor keys and enter key to select
|
||||
the disk you named
|
||||
- Once you have finished installing macOS you will be presented with an
|
||||
the out-of-the-box first-start wizard to configure various options and
|
||||
set up your username and password
|
||||
- OPTIONAL: After you have concluded the out-of-the-box wizard, you may
|
||||
want to enable the TRIM feature that the computer industry created for
|
||||
SSD disks. This feature in our macOS installation will allow QuickEmu
|
||||
to compact (shrink) your macOS disk image whenever you delete files
|
||||
inside the Virtual Machine. Without this step your macOS disk image
|
||||
will only ever get larger and will not shrink even when you delete
|
||||
lots of data inside macOS.
|
||||
- To enable TRIM, open the Terminal application and type the following
|
||||
command followed by pressing <kbd>enter</kbd> to tell macos to use
|
||||
the TRIM command on the hard disk when files are deleted:
|
||||
|
||||
``` shell
|
||||
sudo trimforce enable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will be prompted to enter your account's password to gain the
|
||||
privilege needed. Once you've entered your password and pressed
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> the command will request confirmation
|
||||
in the form of two questions that require you to type
|
||||
<kbd>y</kbd> (for a "yes" response) followed by
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> to confirm.
|
||||
You will be prompted to enter your account’s password to gain the
|
||||
privilege needed. Once you’ve entered your password and pressed
|
||||
<kbd>enter</kbd> the command will request confirmation in the form of
|
||||
two questions that require you to type <kbd>y</kbd> (for a “yes”
|
||||
response) followed by <kbd>enter</kbd> to confirm.
|
||||
|
||||
If you press <kbd>enter</kbd> without first typing
|
||||
<kbd>y</kbd> the system will consider that a negative
|
||||
response as though you said "no":
|
||||
If you press <kbd>enter</kbd> without first typing <kbd>y</kbd> the
|
||||
system will consider that a negative response as though you said “no”:
|
||||
|
||||
``` plain
|
||||
IMPORTANT NOTICE: This tool force-enables TRIM for all relevant attached devices, even though such devices may not have been validated for data integrity while using TRIM. Use of this tool to enable TRIM may result in unintended data loss or data corruption. It should not be used in a commercial operating environment or with important data. Before using this tool, you should back up all of your data and regularly back up data while TRIM is enabled. This tool is provided on an "as is" basis. APPLE MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, REGARDING THIS TOOL OR ITS USE ALONE OR IN COMBINATION WITH YOUR DEVICES, SYSTEMS, OR SERVICES. BY USING THIS TOOL TO ENABLE TRIM, YOU AGREE THAT, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, USE OF THE TOOL IS AT YOUR SOLE RISK AND THAT THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO SATISFACTORY QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, ACCURACY AND EFFORT IS WITH YOU.
|
||||
Are you sure you with to proceed (y/N)?
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And a second confirmation once you've confirmed the previous one:
|
||||
And a second confirmation once you’ve confirmed the previous one:
|
||||
|
||||
``` plain
|
||||
Your system will immediately reboot when this is complete.
|
||||
|
|
@ -350,60 +364,59 @@ disk_img="macos-catalina/disk.qcow2"
|
|||
macos_release="catalina"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `guest_os="macos"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for macOS.
|
||||
- `macos_release="catalina"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for a
|
||||
particular macOS release.
|
||||
- For example VirtIO Network and Memory Ballooning are available
|
||||
in Big Sur and newer, but not previous releases.
|
||||
- And VirtIO Block Media (disks) are supported/stable in Catalina
|
||||
and newer.
|
||||
- `guest_os="macos"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for macOS.
|
||||
- `macos_release="catalina"` instructs Quickemu to optimise for a
|
||||
particular macOS release.
|
||||
- For example VirtIO Network and Memory Ballooning are available in
|
||||
Big Sur and newer, but not previous releases.
|
||||
- And VirtIO Block Media (disks) are supported/stable in Catalina and
|
||||
newer.
|
||||
|
||||
# macOS compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
There are some considerations when running macOS via Quickemu.
|
||||
|
||||
- Supported macOS releases:
|
||||
- High Sierra
|
||||
- Mojave
|
||||
- Catalina **(Recommended)**
|
||||
- Big Sur
|
||||
- Monterey
|
||||
- Ventura
|
||||
- Sonoma
|
||||
- `quickemu` will automatically download the required
|
||||
[OpenCore](https://github.com/acidanthera/OpenCorePkg) bootloader
|
||||
and OVMF firmware from [OSX-KVM](https://github.com/kholia/OSX-KVM).
|
||||
- Optimised by default, but no GPU acceleration is available.
|
||||
- Host CPU vendor is detected and guest CPU is optimised
|
||||
accordingly.
|
||||
- [VirtIO Block
|
||||
Media](https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2019/06/macos-qemu-guest/) is
|
||||
used for the system disk where supported.
|
||||
- [VirtIO `usb-tablet`](http://philjordan.eu/osx-virt/) is used
|
||||
for the mouse.
|
||||
- VirtIO Network (`virtio-net`) is supported and enabled on macOS
|
||||
Big Sur and newer, but earlier releases use `vmxnet3`.
|
||||
- VirtIO Memory Ballooning is supported and enabled on macOS Big
|
||||
Sur and newer but disabled for other support macOS releases.
|
||||
- USB host and SPICE pass-through is:
|
||||
- UHCI (USB 2.0) on macOS Catalina and earlier.
|
||||
- XHCI (USB 3.0) on macOS Big Sur and newer.
|
||||
- Display resolution can only be changed via macOS System Preferences.
|
||||
- **Full Duplex audio requires [VoodooHDA
|
||||
OC](https://github.com/chris1111/VoodooHDA-OC) or pass-through a USB
|
||||
audio-device to the macOS guest VM**.
|
||||
- NOTE! [Gatekeeper](https://disable-gatekeeper.github.io/) and
|
||||
[System Integrity Protection
|
||||
(SIP)](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/security/disabling_and_enabling_system_integrity_protection)
|
||||
need to be disabled to install VoodooHDA OC
|
||||
- File sharing between guest and host is available via
|
||||
[virtio-9p](https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9psetup) and [SPICE
|
||||
webdavd](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/phodav/-/merge_requests/24).
|
||||
- Copy/paste via SPICE agent is **not available on macOS**.
|
||||
- Supported macOS releases:
|
||||
- High Sierra
|
||||
- Mojave
|
||||
- Catalina **(Recommended)**
|
||||
- Big Sur
|
||||
- Monterey
|
||||
- Ventura
|
||||
- Sonoma
|
||||
- `quickemu` will automatically download the required
|
||||
[OpenCore](https://github.com/acidanthera/OpenCorePkg) bootloader and
|
||||
OVMF firmware from [OSX-KVM](https://github.com/kholia/OSX-KVM).
|
||||
- Optimised by default, but no GPU acceleration is available.
|
||||
- Host CPU vendor is detected and guest CPU is optimised accordingly.
|
||||
- [VirtIO Block
|
||||
Media](https://www.kraxel.org/blog/2019/06/macos-qemu-guest/) is
|
||||
used for the system disk where supported.
|
||||
- [VirtIO `usb-tablet`](http://philjordan.eu/osx-virt/) is used for
|
||||
the mouse.
|
||||
- VirtIO Network (`virtio-net`) is supported and enabled on macOS Big
|
||||
Sur and newer, but earlier releases use `vmxnet3`.
|
||||
- VirtIO Memory Ballooning is supported and enabled on macOS Big Sur
|
||||
and newer but disabled for other support macOS releases.
|
||||
- USB host and SPICE pass-through is:
|
||||
- UHCI (USB 2.0) on macOS Catalina and earlier.
|
||||
- XHCI (USB 3.0) on macOS Big Sur and newer.
|
||||
- Display resolution can only be changed via macOS System Preferences.
|
||||
- **Full Duplex audio requires [VoodooHDA
|
||||
OC](https://github.com/chris1111/VoodooHDA-OC) or pass-through a USB
|
||||
audio-device to the macOS guest VM**.
|
||||
- NOTE! [Gatekeeper](https://disable-gatekeeper.github.io/) and
|
||||
[System Integrity Protection
|
||||
(SIP)](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/security/disabling_and_enabling_system_integrity_protection)
|
||||
need to be disabled to install VoodooHDA OC
|
||||
- File sharing between guest and host is available via
|
||||
[virtio-9p](https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/9psetup) and [SPICE
|
||||
webdavd](https://gitlab.gnome.org/GNOME/phodav/-/merge_requests/24).
|
||||
- Copy/paste via SPICE agent is **not available on macOS**.
|
||||
|
||||
# macOS App Store
|
||||
|
||||
If you see *"Your device or computer could not be verified"* when you
|
||||
If you see *“Your device or computer could not be verified”* when you
|
||||
try to login to the App Store, make sure that your wired ethernet device
|
||||
is `en0`. Use `ifconfig` in a terminal to verify this.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -430,7 +443,7 @@ automatically and create an optimised virtual machine configuration.
|
|||
This configuration also includes the [VirtIO drivers for
|
||||
Windows](https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/).
|
||||
|
||||
**Windows 8.1** is also supported but doesn't feature any automated
|
||||
**Windows 8.1** is also supported but doesn’t feature any automated
|
||||
installation or driver optimisation.
|
||||
|
||||
`quickget` can also download [Windows 10
|
||||
|
|
@ -448,12 +461,12 @@ quickget windows 11
|
|||
quickemu --vm windows-11.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- All relevant drivers and services should be installed automatically.
|
||||
- A local administrator user account is automatically created, with
|
||||
these credentials:
|
||||
- Username: `Quickemu`
|
||||
- Password: `quickemu`
|
||||
- Complete the installation as you normally would.
|
||||
- All relevant drivers and services should be installed automatically.
|
||||
- A local administrator user account is automatically created, with
|
||||
these credentials:
|
||||
- Username: `Quickemu`
|
||||
- Password: `quickemu`
|
||||
|
||||
Further information is available from the project
|
||||
[wiki](https://github.com/quickemu-project/quickemu/wiki/04-Create-Windows-virtual-machines)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue